Cell Structure and Function
Links
Click here to view Plant and Animal Cells PowerPoints
Great Images of Cells Cell Games Cell Games2 More Cell Games Cells Web quest
Cells Game+ Osmosis working Cell R US Study
Awesome Video on Osmosis Diffusion Osmosis Song Animations
Cells Game+ Osmosis working Cell R US Study
Awesome Video on Osmosis Diffusion Osmosis Song Animations
Cell Shape and Movement
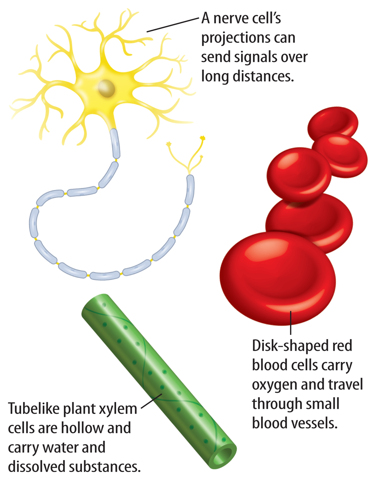
You might recall that all living things are made up of one or more cells. As illustrated in Figure 1, cells come in many shapes and sizes. The size and shape of a cell relates to its job or function. For example, a human red blood cell cannot be seen without a microscope. Its small size and disk shape enable it to pass easily through the smallest blood vessels. The shape of a nerve cell enables it to send signals over long distances. Some plant cells are hollow and make up tube like structures that carry materials throughout a plant.
The structures that make up a cell also have unique functions. Think about how the players on a football team perform different tasks to move the ball down the field. In a similar way, a cell is made of different structures that perform different functions that keep a cell alive. You will read about some of these structures in this lesson.
Cell Membrane
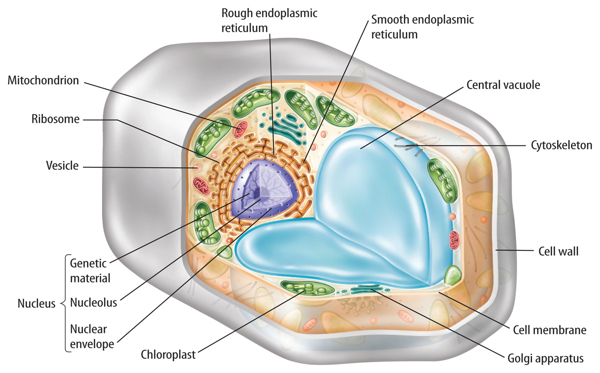
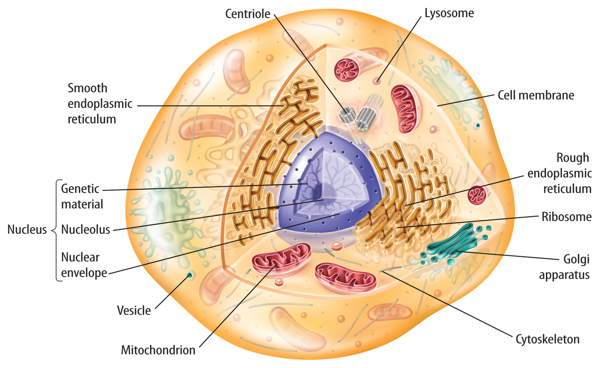
Although different types of cells perform different functions, all cells have some structures in common. As shown in Figure 2 and Figure 3, every cell is surrounded by a protective covering called a membrane. The cell membrane is a flexible covering that protects the inside of a cell from the environment outside a cell. Cell membranes are mostly made of two different macromolecules—proteins and a type of lipid called phospholipids. Think again about a football team. The defensive line tries to stop the other team from moving forward with the football. In a similar way, a cell membrane protects the cell from the outside environment.
How does the cell get nutrients? The cell membrane...
Diffusion is process of things moving in and out of the cell membrane to maintain homeostasis (balance). Osmosis is diffusion with water.
The amount of water and nutrients inside and outside the cell determines the flow of water through the membrane.
Hypotonic Isotonic Hypertonic
more water less solute equal amounts of solute and water more solute, less water
water leaves nothing happens water enters membrane
1.  Reading Check What are cell membranes made of?
Reading Check What are cell membranes made of?
 Reading Check What are cell membranes made of?
Reading Check What are cell membranes made of?
Figure 3 The cytoskeleton maintains the shape of an animal cell.
 Visual Check Compare this animal cell to the plant cell in Figure 2.
Visual Check Compare this animal cell to the plant cell in Figure 2.
Cell Wall
Every cell has a cell membrane, but some cells are also surrounded by a structure called the cell wall. Plant cells such as the one in Figure 2, fungal cells, bacteria, and some types of protists have cell walls. A cell wall is a stiff structure outside the cell membrane. A cell wall protects a cell from attack by viruses and other harmful organisms. In some plant cells and fungal cells, a cell wall helps maintain the cell’s shape and gives structural support.
Cell Appendages
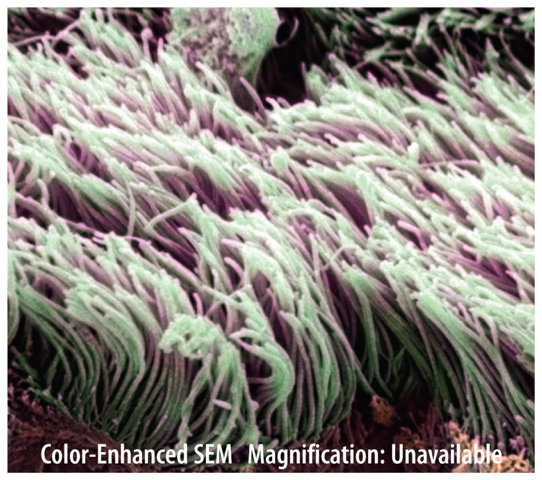
Arms, legs, claws, and antennae are all types of appendages. Cells can have appendages too. Cell appendages are often used for movement. Flagella (fluh JEH luh; singular, flagellum) are long, tail-like appendages that whip back and forth and move a cell. A cell can also have cilia (SIH lee uh; singular, cilium) like the ones shown in Figure 4. Cilia are short, hairlike structures. They can move a cell or move molecules away from a cell. A microscopic organism called a paramecium (pa ruh MEE shee um) moves around its watery environment using its cilia. The cilia in your windpipe move harmful substances away from your lungs.
Cytoplasm and the Cytoskeleton
You might recall that water is the main ingredient in a cell. Most of this water is in the cytoplasm, a fluid inside a cell that contains salts and other molecules. The cytoplasm also contains a cell’s cytoskeleton. The cytoskeleton is a network of threadlike proteins that are joined together. The proteins form a framework inside a cell. This framework gives a cell its shape and helps it move. Cilia and flagella are made from the same proteins that make up the cytoskeleton.
ACADEMIC VOCABULARY
function
(noun) the purpose for which something is used
(noun) the purpose for which something is used
WORD ORIGIN
cytoplasm
from Greek kytos, means “hollow vessel”; and plasma, means “something molded”
from Greek kytos, means “hollow vessel”; and plasma, means “something molded”
Cell Types
Recall that the use of microscopes enabled scientists to discover cells. With more advanced microscopes, scientists discovered that all cells can be grouped into two types— prokaryotic (proh ka ree AH tihk) cells and eukaryotic (yew ker ee AH tihk) cells.
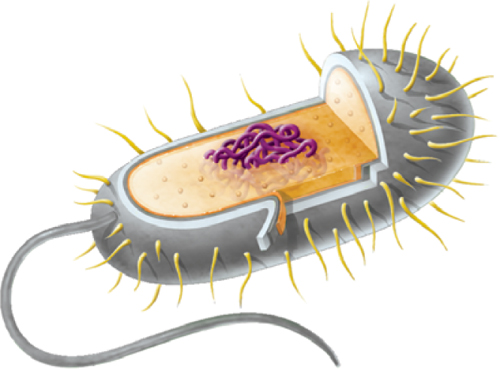
Prokaryotic Cells
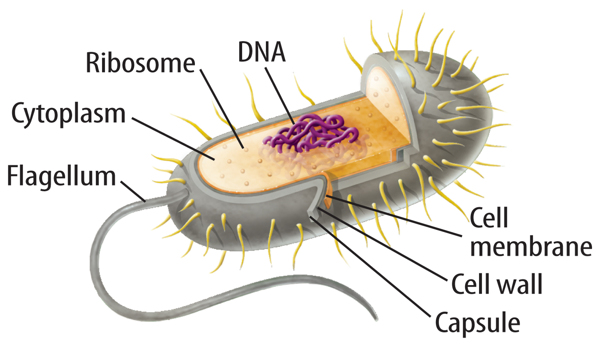
The genetic material in a prokaryotic cell is not surrounded by a membrane, as shown in Figure 5. This is the most important feature of a prokaryotic cell. Prokaryotic cells also do not have many of the other cell parts that you will read about later in this lesson. Most prokaryotic cells are unicellular organisms and are called prokaryotes.
Eukaryotic Cells
Plants, animals, fungi, and protists are all made of eukaryotic cells, such as the ones shown in Figure 2 and Figure 3, and are called eukaryotes. With few exceptions, each eukaryotic cell has genetic material that is surrounded by a membrane. Every eukaryotic cell also has other structures, called organelles,which have specialized functions. Most organelles are surrounded by membranes.
Eukaryotic cells are usually larger than prokaryotic cells. About ten prokaryotic cells would fit inside one eukaryotic cell.
1. Key Concept Check How are prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells similar, and how are they
different?
Cell Organelles
As you have just read, organelles are eukaryotic cell structures with specific functions. Organelles enable cells to carry out different functions at the same time. For example, cells can obtain energy from food, store information, make macromolecules, and get rid of waste materials all at the same time because different organelles perform the different tasks.
The Nucleus
The largest organelle inside most eukaryotic cells is the nucleus, shown in Figure 6. The nucleus is the part of a eukaryotic cell that directs cell activities and contains genetic information stored in DNA. DNA is organized into structures called chromosomes. The number of chromosomes in a nucleus is different for different species of organisms. For example, kangaroo cells contain six pairs of chromosomes. Most human cells contain 23 pairs of chromosomes.
In addition to chromosomes, the nucleus contains proteins and an organelle called the nucleolus (new KLEE uh lus). The nucleolus is often seen as a large dark spot in the nucleus of a cell. The nucleolus makes ribosomes, organelles that are involved in the production of proteins. You will read about ribosomes later in this lesson.
Surrounding the nucleus are two membranes that form a structure called the nuclear envelope. The nuclear envelope contains many pores. Certain molecules, such as ribosomes and RNA, move into and out of the nucleus through these pores.
1.  Reading Check What is the nuclear envelope?
Reading Check What is the nuclear envelope?
 Reading Check What is the nuclear envelope?
Reading Check What is the nuclear envelope?
Figure 6 The nucleus directs cell activity and is surrounded by a membrane.
Manufacturing Molecules
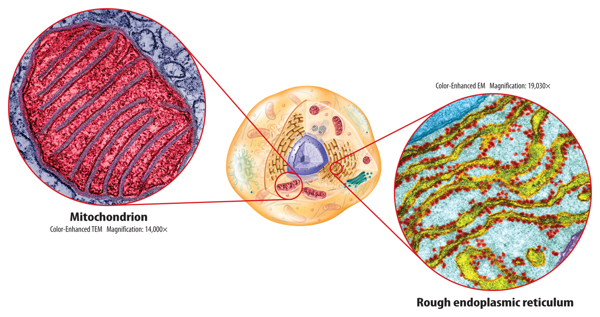
You might recall that proteins are important molecules in cells. Proteins are made on small structures called ribosomes. Unlike other cell organelles, a ribosome is not surrounded by a membrane. Ribosomes are in a cell’s cytoplasm. They also can be attached to a weblike organelle called the endoplasmic (en duh PLAZ mihk • rih TIHK yuh lum), or ER. As shown in Figure 7, the ER spreads from the nucleus throughout most of the cytoplasm. ER with ribosomes on its surface is called rough ER. Rough ER is the site of protein production. ER without ribosomes is called smooth ER. It makes lipids such as cholesterol. Smooth ER is important because it helps remove harmful substances from a cell.
2.  Reading Check Contrast smooth ER and rough ER.
Reading Check Contrast smooth ER and rough ER.
 Reading Check Contrast smooth ER and rough ER.
Reading Check Contrast smooth ER and rough ER.
Figure 7 The endoplasmic reticulum is made of many folded membranes. Mitochondria provide a cell with usable energy.
Processing Energy
All living things require energy in order to survive. Cells process some energy in specialized organelles. Most eukaryotic cells contain hundreds of organelles called mitochondria (mi tuh KAHN dree uh; singular, mitochondrion), shown in Figure 7.Some cells in a human heart can contain a thousand mitochondria.
Like the nucleus, a mitochondrion is surrounded by two membranes. Energy is released during chemical reactions that occur in the mitochondria. This energy is stored in high-energy molecules called ATP—adenosine triphosphate (uh DEH nuh seen • tri FAHS fayt). ATP is the fuel for cellular processes such as growth, cell division, and material transport.
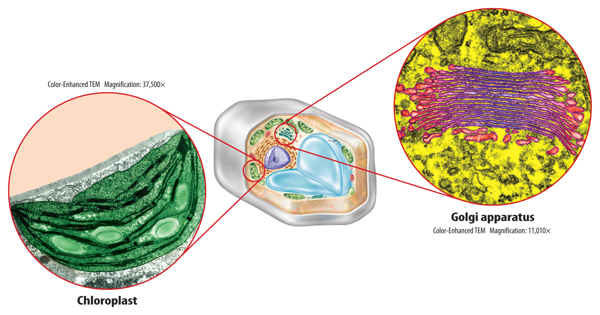
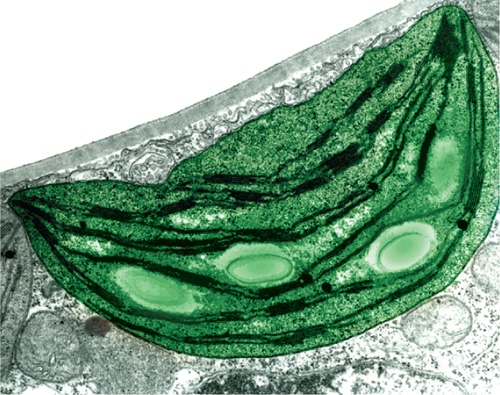
Plant cells and some protists, such as algae, also contain organelles called chloroplasts (KLOR uh plasts), shown in Figure 8. Chloroplasts are membrane-bound organelles that use light energy and make food—a sugar called glucose—from water and carbon dioxide in a process known as photosynthesis (foh toh SIHN thuh sus). The sugar contains stored chemical energy that can be released when a cell needs it.
3.  Reading Check Which types of cells contain chloroplasts?
Reading Check Which types of cells contain chloroplasts?
 Reading Check Which types of cells contain chloroplasts?
Reading Check Which types of cells contain chloroplasts?
Figure 8 Plant cells have chloroplasts that use light energy and make food. The Golgi apparatus packages materials into vesicles.
Processing, Transporting, and Storing Molecules
Near the ER is an organelle that looks like a stack of pancakes. This is the Golgi(GAWL jee) apparatus, shown in Figure 8. It prepares proteins for their specific jobs or functions. Then it packages the proteins into tiny, membrane-bound, ball-like structures called vesicles. Vesicles are organelles that transport substances from one area of a cell to another area of a cell. Some vesicles in an animal cell are called lysosomes. Lysosomes contain substances that help break down and recycle cellular components.
Some cells also have saclike structures called vacuoles (VA kyuh wohlz). Vacuoles are organelles that store food, water, and waste material. A typical plant cell usually has one large vacuole that stores water and other substances. Some animal cells have many small vacuoles.
4. Key Concept Check What is the function of the Golgi apparatus?
SCIENCE USE V. COMMON USE
envelope
Science Use an outer covering
Science Use an outer covering
Common Use a flat paper container for a letter
Lesson Review
Visual Summary
A cell is protected by a flexible covering called the cell membrane.
Cells can be grouped into two types—prokaryotic cells andeukaryotic cells.
In a chloroplast, light energy is used for making sugars in a process called photosynthesis.
Lesson Assessment
Use Vocabulary
1. Distinguish between the cell wall and the cell membrane.
2. Use the terms mitochondria and chloroplasts in a sentence.
3. Define organelle in your own words.
Understand Key Concepts
4. The nucleus of a eukaryotic cell contains genetic information stored in DNA. DNA is organized
into what structures?
into what structures?
A. chromosomes
B. lysosomes
C. mitochondria
D. ribosomes
5. Which organelle is used to store water?
A. chloroplast
B. lysosome
C. nucleus
D. vacuole
6. Explain the role of the cytoskeleton.
7. Draw a prokaryotic cell and label its parts.
8. Compare the roles of the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi apparatus.
9. The arrow below is pointing to which cell part?
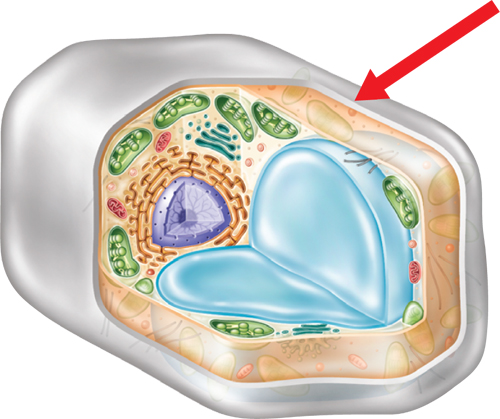

A. chloroplast
B. mitochondrion
C. cell membrane
D. cell wall
10. Which best describes vacuoles?
A. lipids
B. proteins
C. contained in mitochondria
D. storage compartments
11. Which cell shown below can send signals over long distances?
A. 

B. 

C. 

D. 

2. The figure below shows a cell. What is the arrow pointing to?


A. chloroplast
B. cytoplasm
C. mitochondrion
D. nucleus
Interpret Graphics
13. Explain how the structure of the cells below relates to their function.

14. Compare Copy the table below and fill it in to compare the structures of a plant cell to the
structures of an animal cell.
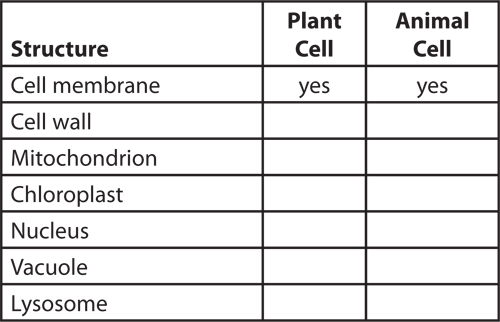
structures of an animal cell.

Critical Thinking
15. List the function of each of the following cell parts: cell membrane, cell wall, chloroplast, cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, mitochondrion, and nucleus.
16. Name the kinds of organisms that have cells with cell walls. Name the kinds of organisms that have cells without cell walls. Briefly describe the benefits of cell walls for organisms.
17. Draw simple diagrams of an animal cell and a plant cell. Label the nucleus, the cytoplasm, the mitochondria, the cell membrane, the chloroplasts, the cell wall, and the central vacuole in the appropriate cells. Briefly describe the main differences between the two cells.
18. Analyze Why are most organelles surrounded by membranes?
19. Compare the features of eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells.
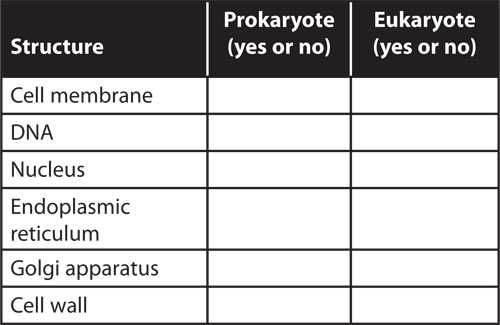
20. Compare prokaryotes and eukaryotes by copying and filling in the table below.

21. The photo below shows a protozoan. What structures enable it to get food into its mouth?
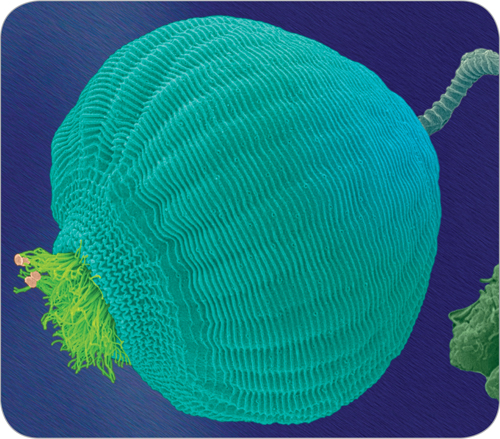

Dr. Dennis Kunkel/Visuals Unlimited/Getty Images
Writing in Science
22. Write a five sentence paragraph relating the cytoskeleton to the walls of a building. Be sure to include a topic sentence and a concluding sentence in your paragraph.



No comments:
Post a Comment