Cells and Life
• How did scientists’ understanding of cells develop?
• What basic substances make up a cell?
• What basic substances make up a cell?
Links
Cells-Lesson 1 Cells Alive Interactive Games cell theory rap Cell Theory Animation
The wacky history of cell theory Cell Theory Timeline BrainPop Cells Short Video Hooke
Games for Extra Credit
Understanding Cells
Have you ever looked up at the night sky and tried to find other planets in our solar system? It is hard to see them without using a telescope. This is because the other planets are millions of kilometers away. Just like we can use telescopes to see other planets, we can use microscopes to see the basic units of all living things—cells. But people didn’t always know about cells. Because cells are so small, early scientists had no tools to study them. It took hundreds of years for scientists to learn about cells.
More than 300 years ago, an English scientist named Robert Hooke built a microscope. He used the microscope to look at cork, which is part of a cork oak tree’s bark. What he saw looked like the openings in a honeycomb, as shown in Figure 1. The openings reminded him of the small rooms, called cells, where monks lived. He called the structures cells, from the Latin word cellula (SEL yuh luh), which means “small rooms.”
Figure 1 To Robert Hooke, the cells of cork looked like the openings in a honeycomb.
The Cell Theory
After Hooke’s discovery, other scientists began making better microscopes and looking for cells in many other places, such as pond water and blood. The newer microscopes enabled scientists to see different structures inside cells. Matthias Schleiden (SHLI dun), a German scientist, used one of the new microscopes to look at plant cells. Around the same time, another German scientist, Theodor Schwann, used a microscope to study animal cells. Schleiden and Schwann realized that plant and animal cells have similar features and carry on similarfunctions, such as extracting energy from food and eliminating wastes. From this evidence, Schleiden and Schwann concluded that cells are the basic unit of life.
Almost two decades later, Rudolf Virchow (VUR koh), a German doctor, proposed that all cells come from preexisting cells, or cells that already exist.The observations made by Schleiden, Schwann, and Virchow were combined into one theory.
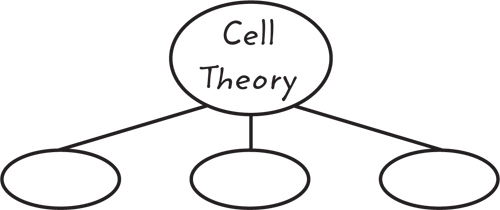
As illustrated in Table 1, the cell theory states that all living things are made ofone or more cells, the cell is the smallest unit of life, and all new cells comefrom preexisting cells. After the development of the cell theory, scientists raised more questions about cells. If all living things are made of cells, what are cells made of?
1. Key Concept Check How did scientists’ understanding of cells develop?
(tl) Tim Fitzharris/Minden Pictures/Getty Images, (tr) James M. Bell/Photo Researchers, (c) Biophoto Associates/Photo Researchers, (bl, bc, br) Dr. Richard Kessel & Dr. Gene Shih/Visuals Unlimited/Getty Images
Table 1 Scientists developed the cell theory after studying cells with microscopes.
In-Class Activity: Cell Theory Time Line
As a class, create a time line of the important discoveries that led to the development of the cell theory. Draw a time line on the board or chart paper. Add entries at the appropriate time points. For each entry on the time line, note the scientist and any relevant facts about the discovery. Once the time line is complete, copy the diagram in your Science Journal to help you understand the key principles of the cell theory.
Analyze and Conclude
1. What invention enabled scientists to study cells and develop the cell theory?
2. Which three scientists discovered evidence that led directly to the development of the cell theory?
3. What are the three principles of the cell theory?
REVIEW VOCABULARY
theory
explanation of things or events based on scientific knowledge resulting from many observations and experiments
explanation of things or events based on scientific knowledge resulting from many observations and experiments
Basic Cell Substances
Have you ever watched a train travel down a railroad track? The locomotive pulls train cars that are hooked together. Like a train, many of the substances in cells are made of smaller parts that are joined together. These substances, calledmacromolecules, form by joining many small molecules together. As you will read later in this lesson, macromolecules have many important roles in cells. But macromolecules cannot function without one of the most important substances in cells—water.
The Main Ingredient—Water
The main ingredient in any cell is water. It makes up more than 70 percent of a cell’s volume and is essential for life. Why is water such an important molecule? In addition to making up a large part of the inside of cells, water also surrounds cells. The water surrounding your cells helps to insulate your body, which maintains homeostasis, or a stable internal environment.
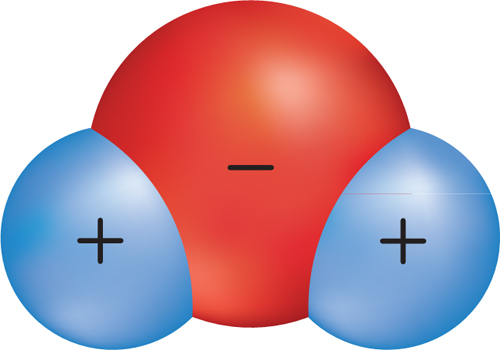
The structure of a water molecule makes it ideal for dissolving many other substances. Substances must be in a liquid to move into and out of cells. A water molecule has two areas:
• An area that is more negative (−), called the negative end; this end can attract the positive part of
another substance.
another substance.
• An area that is more positive (+), called the positive end; this end can attract the negative part of
another substance.
another substance.
Examine Figure 2 to see how the positive and negative ends of water molecules dissolve salt crystals.

FoodCollection/SuperStock
Figure 2 The positive and negative ends of a water molecule attract the positive and negative parts of another substance, similar to the way magnets are attracted to each other.
 Visual Check Which part of the salt crystal is attracted to the oxygen in the water molecule?
Visual Check Which part of the salt crystal is attracted to the oxygen in the water molecule?
Macromolecules
Although water is essential for life, all cells contain other substances that enable them to function. Recall that macro-molecules are large molecules that form when smaller molecules join together. As shown in Figure 3, there are four types of macromolecules in cells: nucleic acids, proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates. Each type of macromolecule has unique functions in a cell. These functions range from growth and communication to movement and storage.
Nucleic Acids Both deoxyribonucleic (dee AHK sih ri boh noo klee ihk) acid (DNA) and ribonucleic (ri boh noo KLEE ihk) acid (RNA) are nucleic acids. Nucleic acidsare macromolecules that form when long chains of molecules called nucleotides (NEW klee uh tidz) join together. The order of nucleotides in DNA and RNA is important. If you change the order of words in a sentence, you can change the meaning of the sentence. In a similar way, changing the order of nucleotides in DNA and
RNA can change the genetic information in a cell.
Nucleic acids are important in cells because they contain genetic information. This information can pass from parents to offspring. DNA includes instructions for cell growth, cell reproduction, and cell processes that enable a cell to respond to its environment. DNA is used to make RNA. RNA is used to make proteins.
Proteins The macromolecules necessary for nearly everything cells do are proteins. Proteins are long chains of amino acid molecules. You just read that RNA is used to make proteins. RNA contains instructions for joining amino acids together.
Cells contain hundreds of proteins. Each protein has a unique function. Some proteins help cells communicate with each other. Other proteins transport substances around inside cells. Some proteins, such as amylase (AM uh lays) in saliva, help break down nutrients in food. Other proteins, such as keratin (KER uh tun)—a protein found in hair, horns, and feathers—provide structural support.
Lipids Another group of macromolecules found in cells is lipids. A lipid is a large macromolecule that does not dissolve in water. Because lipids do not mix with water, they play an important role as protective barriers in cells. They are also the major part of cell membranes. Lipids play roles in energy storage and in cell communication. Examples of lipids are cholesterol (kuh LES tuh rawl), phospholipids (fahs foh LIH pids), and vitamin A.
1.  Reading Check Why are lipids important to cells?
Reading Check Why are lipids important to cells?
 Reading Check Why are lipids important to cells?
Reading Check Why are lipids important to cells?
Carbohydrates One sugar molecule, two sugar molecules, or a long chain of sugar molecules make up carbohydrates (kar boh HI drayts). Carbohydrates store energy, provide structural support, and are needed for communication between cells. Sugars and starches are carbohydrates that store energy. Fruits contain sugars. Breads and pastas are mostly starch. The energy in sugars and starches can be released quickly through chemical reactions in cells. Cellulose is a carbohydrate in the cell walls in plants that provides structural support.
2. Key Concept Check What basic substances make up a cell?
Figure 3 Each type of macromolecule has a special function in a cell.
WORD ORIGIN
macromolecule
from Greek makro–, means “long”; and Latin molecula, means “mass”
from Greek makro–, means “long”; and Latin molecula, means “mass”
Visual Summary
The cell theory summarizes the main principles for understanding that thecell is the basic unit of life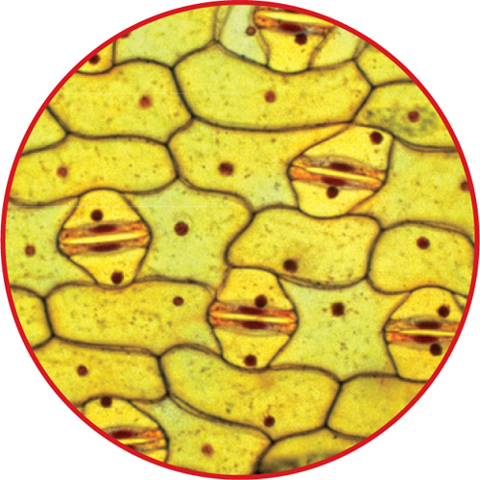

James M. Bell/Photo Researchers
Water is the main ingredient in every cell.
A nucleic acid, such as DNA, contains the genetic information for a cell.
What do you think NOW?
You first read the statements below at the beginning of the lesson.
1. Nonliving things have cells.
2. Cells are made mostly of water.
Did you change your mind about whether you agree or disagree with the statements? Rewrite any false statements to make them true.
Lesson Assessment
Use Vocabulary
1. The __________ __________ states that the cell is the basic unit of all living things.
2. Distinguish between a carbohydrate and a lipid.
3. Use the term nucleic acid in a sentence.
Understand Key Concepts
4. Which macromolecule is made from amino acids?
A. lipid
B. protein
C. carbohydrate
D. nucleic acid
5. Describe how the invention of the microscope helped scientists understand cells
6. Compare the functions of DNA and proteins in a cell.
7. Cholesterol is which type of macromolecule?
A. carbohydrate
B. lipid
C. nucleic acid
D. protein
8. Genetic information is stored in which macromolecule?
A. DNA
B. glucose
C. lipid
D. starch
Interpret Graphics
9. Summarize Copy and fill in the graphic organizer below to summarize the main principles of the cell theory.

10. Analyze How does the structure of the water molecule shown below enable it to interact with other water molecules?


Critical Thinking
11. Summarize the functions of lipids in cells.
12. Hypothesize why carbohydrates are found in plant cell walls.
13. Evaluate the importance of the microscope to biology.
14. Summarize the role of water in cells.
15. Hypothesize how new cells form from existing cells.
16. Assess According to the cell theory, the cell is the smallest unit of life. How does this concept relate to the function of cells?



No comments:
Post a Comment