EVOLUTION & Adaptation
Links
Visit this website to learn and play - Darwin's Theory
Do Plants communicate? Racoons in the city
Ape Genius!
Hunting & escaping
Friendly Gut Bacteria
Origin of Life
The Living Planet - Life and extinction
Heredity & Traits Natural Selection More on Natural Selection
Natural Selection & Artificial Breeding Mating Season Chicken Genetics
Video - Ape Genius
Lessons About Heredity and Variation
Weird Science and MutationsGenetic Abnormalities or Experiments
10 Controversial Genetic Experiments
Research different animals and how they have adapted here
Please watch the video below and write one paragraph about 1 of the genetic discoveries.http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZYpGI54JKf4
Understand Key Concepts
Interpret Graphics
Critical Thinking
Writing in Science
Links
Visit this website to learn and play - Darwin's Theory
Do Plants communicate? Racoons in the city
Ape Genius!
Hunting & escaping
Friendly Gut Bacteria
Origin of Life
The Living Planet - Life and extinction
Heredity & Traits Natural Selection More on Natural Selection
Natural Selection & Artificial Breeding Mating Season Chicken Genetics
Video - Ape Genius
Lessons About Heredity and Variation
Weird Science and MutationsGenetic Abnormalities or Experiments
10 Controversial Genetic Experiments
Research different animals and how they have adapted here
Please watch the video below and write one paragraph about 1 of the genetic discoveries.http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZYpGI54JKf4
Diversity of Organisms
Have you ever wondered how Earth came to have a diversity of living things? Millions of different types, or species, of organisms exist on Earth. Each species has its own set of traits. All species of fish have fish traits, and all species of birds have bird traits. However, not all fish have the same fish traits, nor do all birds have the same bird traits. As shown in Figure 1, penguins and hummingbirds both have wings, feathers, and beaks. Yet these traits are very different. How can these species be so different and yet have similar traits?
In the early 1800s, the puzzle of diversity captured the attention of a young naturalist in England named Charles Darwin. A naturalist studies the history and varieties of life. Over many years of studying many different life forms, Darwin developed a scientific theory that helped him understand how one group of organisms can be different yet have similar traits. As you will read, Darwin’s theory, called the theory of evolution by natural selection, explains how traits and species can change over time.
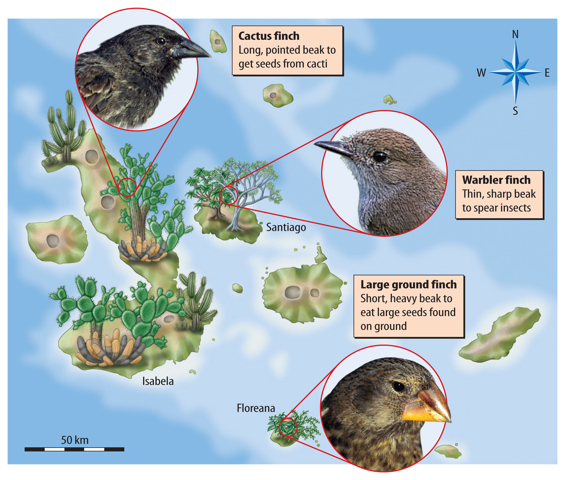
In 1831, when Darwin was a young man, he began a five-year journey around the world. During this journey, Darwin observed and collected many animals and plants. Among them was a group of finches from the Galápagos Islands, which are off the coast of South America. Darwin was fascinated by the different environments of these islands. As shown in Figure 2, the environment on some islands was dry and had cacti (singular, cactus). Others had a moist environment and trees.
Figure 2 Each finch that Darwin collected had a beak specialized for a particular environment and diet.
1.  Visual Check What makes the cactus finch’s beak best suited to eat cactus seeds?
Visual Check What makes the cactus finch’s beak best suited to eat cactus seeds?
 Visual Check What makes the cactus finch’s beak best suited to eat cactus seeds?
Visual Check What makes the cactus finch’s beak best suited to eat cactus seeds?
Darwin’s Finches
The finches that Darwin collected on the islands were all about the same size and color, but the finches had different beaks. The beaks were so different that Darwin considered each type of bird as a separate species. When he returned to England, Darwin realized that each species of finch he collected had come from a different island. He noticed that each species of finch was specialized, or suited, for living in a particular environment and eating the food found there.
REVIEW VOCABULARY
competition
the struggle among organisms for food, space, and other requirements
the struggle among organisms for food, space, and other requirements
After years of studying the Galápagos finches, Darwin proposed that the different finch species developed over a long period of time from one group of finches. He proposed that this group had arrived on one of the islands many generations ago. Perhaps a storm carried it over from the mainland.
Over time, as the finch population grew, the finches moved to the other islands. Soon, the food and other resources on each island began to run out. The finches had to compete with each other to survive. The finches with traits that made them better competitors for resources in their environments lived longer. They also produced more offspring than those that did not have those traits. This is the core of Darwin’s theory of evolution by natural selection. During the process of natural selection, organisms with traits best suited to their environment are most likely to survive and reproduce.
1.  Reading Check Why is competition important to natural selection?
Reading Check Why is competition important to natural selection?
 Reading Check Why is competition important to natural selection?
Reading Check Why is competition important to natural selection?
Variations
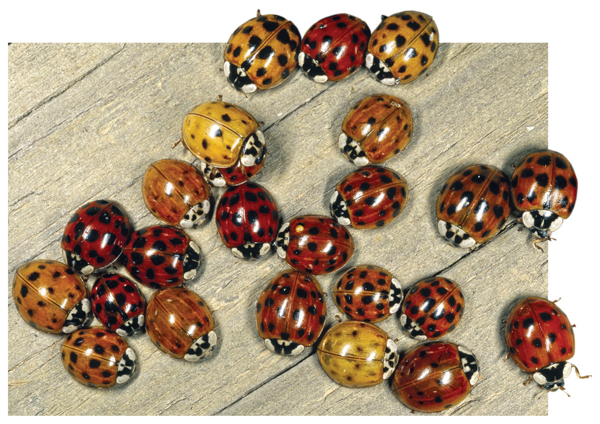
The finch species were suited to their different island environments because of the differences in their beaks. These differences developed over time partly because each member of a species is slightly different. In Figure 3, each beetle has slight variations (ver ee AY shunz) in its appearance even though all the beetles are members of the same species. A variation is a small change in a trait that makes an individual slightly different from other members of its species.
Figure 3 These beetles are all members of the same species. Yet each has slight variations.
Source of Variations
Where do variations come from? You read earlier that a mutation is a change in a gene. Sometimes, a mutation can change an organism’s phenotype. When it does, it gives the organism a variation.
Variations and Survival
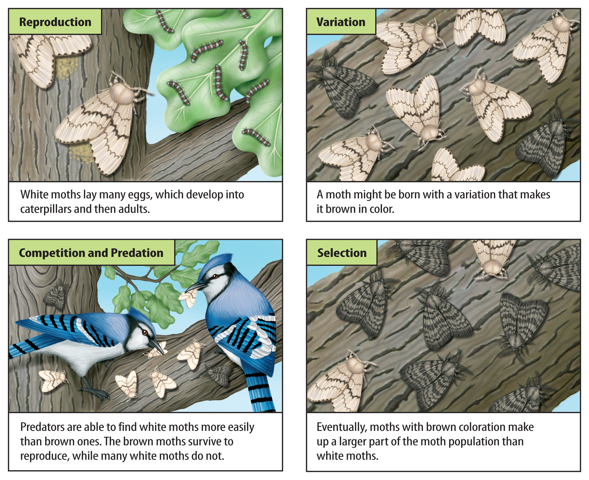
Some variations that arise from mutations can hurt an organism. Others might help an organism live longer. For example, a variation might make an organism better able to find food or help it avoid being caught by a predator. An individual organism that lives longer has a greater chance of reproducing and passing a variation to its offspring. Over time, as more and more offspring are born with the variation, the variation becomes a trait of the population. Natural selection might produce a beneficial color variation in a population of moths like the one shown in Figure 4.
2. Key Concept Check How might a variation be beneficial to an organism?
WORD ORIGIN
variation
from Latin variationem, means “a difference”
from Latin variationem, means “a difference”
Math Skills: Use Statistics
The mean of a set of data is the arithmetic average. To find the mean of a group of numbers:
1. find the sum of all the numbers; and
2. divide the sum by the number of items in the set.
For example, a hawk catches 10 mice on the first day, 8 on the second day, and 12 on the third day. The mean number of mice caught by the hawk is equal to 10 + 8 + 12 divided by 3 days. (30 mice/3 days = 10 mice/day.)
1. Practice
The life spans of a group of worker bees were 34, 28, 39, 27, 24, 35, 30, and 29 days. What is the mean life span of the bees?
The life spans of a group of worker bees were 34, 28, 39, 27, 24, 35, 30, and 29 days. What is the mean life span of the bees?
1
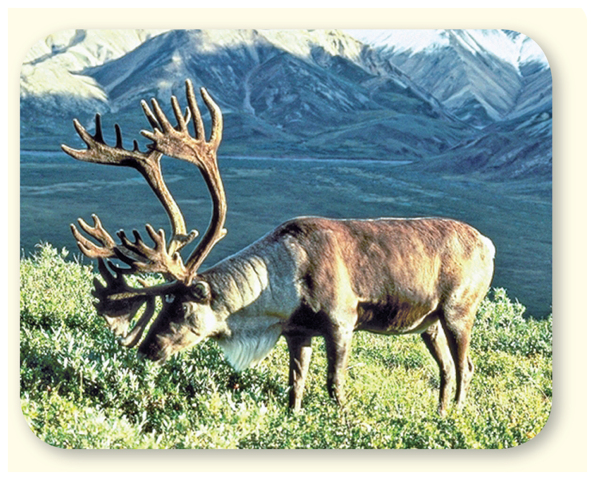
Caribou, like the one in the photo below, are a species of large deer that live on the tundra. A tundra is a cold region where summers are very short and few trees grow. Not many organisms can survive there.
1. Each member of your group will suggest one variation to the caribou’s physical characteristics that might help it adapt to the environment where you live. The next person should try to improve on that variation or think of a new variation.
2. Make a list of the variations suggested and how each variation might help caribou adapt to your environment in your Science Journal.
Analyze and Conclude
1. Infer how the characteristics of caribou make them well suited to their tundra environment.
2. Hypothesize what might happen to caribou if their environment changed but variations did not occur within individual members of the species.
3. Key Describe how some internal and external variations might help an organism survive while other variations might not help an organism survive. Be sure to give examples of both internal and external variations in your description.
Genes that express favorable variations can be passed to future generations. Over long periods of time, this process results in species of organisms with special traits called adaptations. An adaptation is an inherited trait that increases an organism’s chance of surviving and reproducing in a particular environment.
Adaptations can be physical traits or behavioral traits. Green tree frogs, such as the one shown in Figure 5, have long, sticky tongues. This is a physical adaptation that helps the frogs catch insects. Vascular plants have xylem, which are internal hollow tubes. This physical adaptation enables the transport of water throughout the plants. A behavioral adaptation involves actions rather than body structure. Mass movement, or migration, is a behavioral adaptation that helps some species survive. For example, blue whales migrate thousands of kilometers each year. They mate and give birth in the tropics during the winter, then migrate to summer feeding grounds in the Arctic or the Antarctic.
1. Key Concept Check What is the difference between an adaptation and a trait?
Finding Food
All species have adaptations that help them find food. Many of these adaptations involve the senses. Hawks and eagles have excellent eyesight. They see their prey while flying high above the ground. Other animals, including sharks, anteaters, and raccoons, use their keen sense of smell to find food.
Mouthpart adaptations help individuals of many species eat their food. Recall that the beaks of Darwin’s finches were specialized for eating the different foods on their islands. Examples of mouthpart adaptations in insects are shown in Figure 6.
Avoiding Predators
Avoiding being eaten is as important as finding food to eat. Structures on some species, such as sharp quills on porcupines or thorns on roses, discourage predators. Other organisms contain chemicals on their bodies or leaves that make them taste bad to predators.
Other species have adaptations that help them hide from or trick predators. A leafy sea dragon, like the one shown at the beginning of this lesson, resembles the kelp in its environment. The ability to blend in with the environment is called camouflage (KA muh flahj). Camouflage makes an animal hard for a predator to see. Another adaptation that tricks predators is shown in Figure 7.
2. Key Concept Check How does camouflage help members of a species survive?
Movement
Most species of organisms move to find food and avoid predators. Even some species that spend most of their lives in one place, like the barnacle shown in Figure 8, have adaptations for movement. Muscle and bone adaptations such as fins, wings, and long legs enable many species of animals to swim, fly, or run. Some unicellular species of organisms, such as Paramecia, move by beating tiny hairlike cilia (SIH lee uh).
Though plants cannot move from place to place, some species can turn and follow the Sun’s path across the sky. This adaptation helps them receive the maximum amount of sunlight. Adaptations in seeds enable some plant species to disperse their offspring across great distances. For example, sticky seeds can attach to animals, and as the animals move from place to place they deposit the seeds. Seeds such as dandelion seeds can be carried by the wind.
Many species are well adapted to move in one environment but poorly adapted to move in another. Have you ever seen a penguin walk? Penguins have flippers that help them swim fast in the water, where they find their food. On land, they are clumsy walkers.
Surviving Extremes
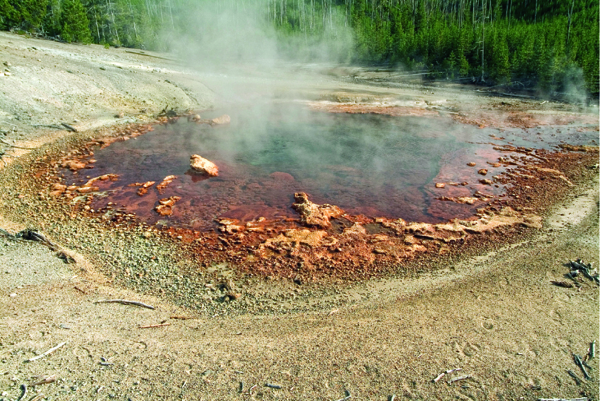
Some species must adapt to freezing temperatures, drought, or other environmental extremes in order to survive. The cacti that inhabit desert environments have special stems that store water. Polar bears have layers of fat that insulate them, protecting them from air temperatures that can reach −45°C. Some animal species, such as brown bats and snakes, adapt to cold weather by becoming much less active. Adaptations have enabled life-forms to live in some of Earth’s most extreme environments, such as the ones shown in Figure 9.
Figure 9 Because of their adaptations, some species can live in extremely cold or hot environments.
In areas of extreme cold, such as the one with icebergs shown above, species such as the ice fish live in water as cold as −2°C, but its blood doesn't freeze because it contains a substance similar to antifreeze.
In areas of extreme heat, such as the hot springs in Yellowstone National Park shown above, special proteins enable some species to thrive in the hot springs where temperatures can reach 100°C.
In areas of extreme cold, such as the one with icebergs shown above, species such as the ice fish live in water as cold as −2°C, but its blood doesn't freeze because it contains a substance similar to antifreeze.
In areas of extreme heat, such as the hot springs in Yellowstone National Park shown above, special proteins enable some species to thrive in the hot springs where temperatures can reach 100°C.
ACADEMIC VOCABULARY
migration
(noun) instinctive, seasonal movement of animals from one place to another
(noun) instinctive, seasonal movement of animals from one place to another
You have read that species of organisms adapt to their environments through the process of natural selection. In this process, changes to genes that help an organism survive accumulate over time. Humans can also change an organism’s genes by choosing which organisms will reproduce. This process is called selective breeding. Selective breeding is the deliberate breeding of plants or animals for desired traits. Breeders select plants or animals that have a specific trait. They then breed them so that their offspring will have the desired trait. Over many generations, the resulting organisms can have a phenotype and a genotype very different from the original ancestor.
1. Key Concept Check How are changes caused by selective breeding different from changes caused by the environment?
Agriculture
Most of the food you eat is the result of selective breeding. For example, cows are bred for meat quality or increased milk production. Some chickens are bred for increased egg production. Fruits and vegetables are selectively bred for traits that enable them to tolerate cold, have a better taste, or grow larger. The ear of corn shown in Figure 10 is much bigger than the ear of its ancestor, teosinte (tay oh SIN tee).
Pets
Do you have a dog or a cat? Most pets have been selectively bred over many years. Domestic cats were bred from wild cats. Dogs were bred from wolves. As shown in Figure 11, dogs today can be so different from each other that it is hard to tell they all belong to the same species.
Lesson Review
Visual Summary
Natural selection means that organisms with traits best suited to their environment are the most likely to survive and reproduce.
Over time, variations in a population can result in adaptations.
Humans can influence traits in plants and animals through selective breeding.
What do you think NOW?
You first read the statements below at the beginning of the lesson.
1. Charles Darwin’s observations of bird beaks helped him develop his theory of natural selection.
2. Mutations are harmful.
3. When humans breed cows that produce more milk, there is no change to the offspring’s genes.
Did you change your mind about whether you agree or disagree with the statements? Rewrite any false statements to make them true.
Lesson Assessment
Use Vocabulary
1. Use the term variation in a sentence.
2. Define adaptation in your own words.
3. Darwin’s observations led to the development of the theory of __________ __________.
Understand Key Concepts
4. Discuss how natural selection produces adaptations found in a population of organisms.
5. Compare the processes of natural selection and selective breeding.
6. Which situation has given rise to a trait that could be passed on to offspring?
A.A boat motor cut off the arm of a starfish.
B.A gardener’s application of fertilizer produced large roses.
C.An all-white honeybee was born.
D.A sled dog developed strong muscles.
7. What does the drawing below illustrate?
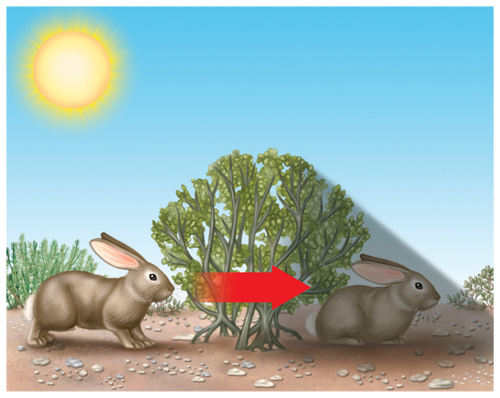

A.a behavioral adaptation
B.a genotype variation
C.a phenotype variation
D.a physical adaptation
8. Which did Charles Darwin observe on the Galápagos Islands?
A.differences in phenotypes in populations
B.genes undergoing the process of mutation
C.new islands being formed
D.selective breeding practices
9. Natural selection results in
A. all harmful traits being eliminated from a population.
B. a population that is adapted to an environment.
C. a perfectly adapted group of organisms.
D. long-lasting adaptations.
10. Which is an example of selective breeding?
A. a farmer that mates his largest pigs
B. fish that swim thousands of kilometers to lay eggs
C. lizards that avoid being preyed upon because they taste bad
D. male and female frogs that blend in with their environment
Interpret Graphics
11. Organize Information Copy and fill in the graphic organizer below to describe ways that
adaptations help organisms survive.
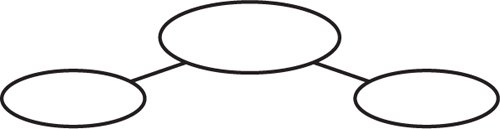
adaptations help organisms survive.

Critical Thinking
12. Explain how the color of the fox in the photo below might be an adaptation.


Creatas/PunchStock
13. InvestigateOne of the internal adaptations birds have is hollow bones. Investigate how this
adaptation enables birds to fly. Write a paragraph describing your findings.
adaptation enables birds to fly. Write a paragraph describing your findings.
14. Explain how mutations and variations are related.
15. Compare and contrast migration in robins and a thick fat layer in polar bears.
16. Argue Mutations are often considered bad. Make an argument for why mutations can be
beneficial.
beneficial.
17. Draw an organism adapted to the following environment: A crystal-clear lake has a sandy
bottom. The oxygen content of the water is low. There are many predators in the lake. Explain
each adaptation.
bottom. The oxygen content of the water is low. There are many predators in the lake. Explain
each adaptation.
18. Interpret Graphics The coral snake below is venomous. The Scarlet king snake is not. Explain
how the Scarlet king snake’s color pattern is an adaptation. What advantage does the adaptation
provide for the king snake?

how the Scarlet king snake’s color pattern is an adaptation. What advantage does the adaptation
provide for the king snake?

19. Why do living things have such diverse traits? Summarize how the theory of natural selection
explains the diversity of one kind of organism, such as fish or trees.
explains the diversity of one kind of organism, such as fish or trees.
20. Identify which traits of the tarsier below are adaptations that help it survive in its dense tropical
environment.
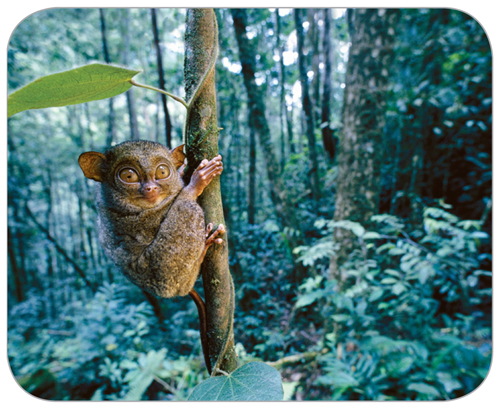

environment.

Frans Lanting/CORBIS
Writing in Science
21. Write a paragraph comparing natural selection and selective breeding. Explain their similarities
and differences using an example of each. Be sure to include a topic sentence and a concluding
sentence.
and differences using an example of each. Be sure to include a topic sentence and a concluding
sentence.
Math Skills
Use Statistics
22. Individuals from a certain species of plant sometimes developed sticky leaves. These leaves
trapped insects feeding on the plant. During several generations, 8, 13, 9, and 12 of these
variations appeared per 100 plants. What was the mean number of plants with this variation?
trapped insects feeding on the plant. During several generations, 8, 13, 9, and 12 of these
variations appeared per 100 plants. What was the mean number of plants with this variation?
Use the following information to answer questions 23 and 24.
The table shows the number of seeds eaten by three different species of finches over a period of time. The species eat similar food and live in the same area.
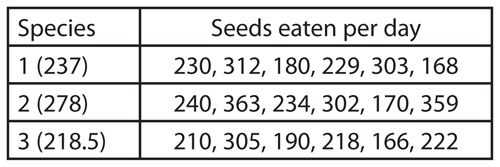

23. Assuming that each finch requires a minimum of 225 seeds per day to survive, which species has
the best chance of survival?
the best chance of survival?
24. Which species is least able to compete for food in its environment?















No comments:
Post a Comment